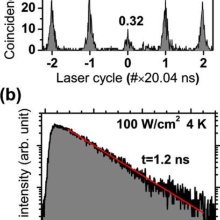
An ultrathin virtual Ge substrate (GeVS) with low defect density was realized on CMOS-compatible Si(001) by molecular beam epitaxy. On top, III–V layers were deposited by metal–organic vapor-phase epitaxy, at which diffusion of Ge was successfully suppressed. Nonclassical light emitters, based on InP quantum dots (QDs), were realized on a thin GaAs buffer (thickness ≈ 1 µm). The quantum dots show emission in the red spectral region, meeting the range of the highest detection efficiency of silicon avalanche photodiodes. The decay dynamics and emission characteristics of single QDs were investigated. Autocorrelation measurements prove single-photon emission with a value of g (2)(0)=0.32.
Publication: Epitaxially Grown Indium Phosphide Quantum Dots on a Virtual Ge Substrate Realized on Si(001)
Michael Wiesner, Moritz Bommer, Wolfgang-Michael Schulz, Martin Etter, Jens Werner, Michael Oehme, Jörg Schulze, Michael Jetter, and Peter Michler ![]() Appl. Phys. Express 5, 042001 (2012)
Appl. Phys. Express 5, 042001 (2012)
Contact person: Dr. M. Jetter