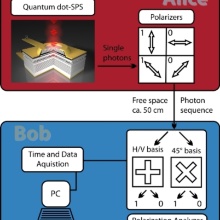
We report on in-lab free space quantum key distribution (QKD) experiments over 40 cm distance using highly efficient electrically driven quantum dot single-photon sources emitting in the red as well as near-infrared spectral range. In the case of infrared emitting devices, we achieve sifted key rates of 27.2 kbit s −1 (35.4 kbit s −1) at a quantum bit error rate (QBER) of 3.9% (3.8%) and a g (2)(0) value of 0.35 (0.49) at moderate (high) excitation. The red emitting diodes generate sifted keys at a rate of 95.0 kbit s −1 at a QBER of 4.1% and a g (2)(0) value of 0.49. This first successful proof of principle QKD experiment based on electrically operated semiconductor single-photon sources can be considered as a major step toward practical and efficient quantum cryptography scenarios.
Publication: Quantum key distribution using quantum dot single-photon emitting diodes in the red and near infrared spectral range
Tobias Heindel, Christian A Kessler, Markus Rau, Christian Schneider, Martin Fürst, Fabian Hargart, Wolfgang-Michael Schulz, Marcus Eichfelder, Robert Roßbach, Sebastian Nauerth, Matthias Lermer, Henning Weier, Michael Jetter, Martin Kamp, Stephan Reitzenstein, Sven Höfling, Peter Michler, Harald Weinfurter and Alfred Forchel ![]() New J. Phys. 14, 083001 (2012)
New J. Phys. 14, 083001 (2012)
Contact person: Prof. Peter Michler